The Bureau Labor Statistics was founded in 1884. This national statistical agency gathers, analyzes and disseminates important economic information. It performs data analysis and research on a broad range of economic issues such as labor demand, prices. employment, wages and the labor force. The agency also publishes statistical reports, and provides training on labor statistics to other countries.
To monitor wages and employment, the Bureau Labor Statistics conducts labor force surveys. It generates detailed industry estimates about nonfarm employment, as well wage rates. It also produces the Consumer Price Index, which measures prices of common consumer goods. The Bureau also measures changes in prices throughout the economy, including transport, housing and healthcare.
BLS publishes data regarding employment and wages for the United States as well as several other areas. These data are regularly cited and referred to by economists, market participants, and businesses. In addition to these reports the Bureau produces statistical tables which provide detailed information about economic conditions. The Consumer Price Index is the most significant report. The Bureau also produces other economic data, such as the Producers Price Index and the Employment Situation Report.

The Bureau of Labor Statistics performs research about the employment of men, women, and seniors. It also produces data on worker fatalities and nonfatal workplace injuries. It also maintains data files about low-wage workers. The Bureau also conducts research on foreign-owned establishments that have at least 10% of their stock owned by foreigners.
The Bureau also publishes information on the national rate of unemployment, which is derived largely from the Current Population Survey. The Bureau also publishes several supplemental surveys. Current Employment Statistics, (CES) surveys approximately 670,000 worksites. BLS also conducts research about the country's labor organizations and businesses.
The Bureau also publishes the Employment and Earnings report, which provides a national outlook of the labor market. This report gives information on the unemployment rate, total employment and wages as well as how employment is growing. The Bureau also publishes a list of the fastest-growing jobs. The Bureau also offers listings of high-wage jobs.
The Bureau has an extensive staff. It also has six regional offices. The Bureau also has several other smaller local offices.

The Bureau also publishes several reports, including the National Compensation Survey. The National Compensation Survey is the most important data collection program in the United States. This program provides data on average earnings, hours and wages for all employees in all industries. This data is then aggregated into an industry average. The report is published quarterly in many industries. The Occupational Outlook Quarterly also provides analysis on the labor market for certain occupations.
The Bureau also hosts an Office of Prices and Living Conditions. It measures changes in price prices. The Producer Price Index and Consumer Price Index both come from the Office of Prices and Living Conditions. It also provides information on import and exported prices.
FAQ
What does the term manufacturing industries mean?
Manufacturing Industries are companies that manufacture products. Consumers are the people who purchase these products. These companies use a variety processes such as distribution, retailing and management to accomplish their purpose. They make goods from raw materials with machines and other equipment. This includes all types manufactured goods such as clothing, building materials, furniture, electronics, tools and machinery.
How can I find out more about manufacturing?
Hands-on experience is the best way to learn more about manufacturing. You can also read educational videos or take classes if this isn't possible.
What is the distinction between Production Planning or Scheduling?
Production Planning (PP), is the process of deciding what production needs to take place at any given time. This can be done by forecasting demand and identifying production capabilities.
Scheduling is the process of assigning specific dates to tasks so they can be completed within the specified timeframe.
Statistics
- Many factories witnessed a 30% increase in output due to the shift to electric motors. (en.wikipedia.org)
- In the United States, for example, manufacturing makes up 15% of the economic output. (twi-global.com)
- You can multiply the result by 100 to get the total percent of monthly overhead. (investopedia.com)
- According to a Statista study, U.S. businesses spent $1.63 trillion on logistics in 2019, moving goods from origin to end user through various supply chain network segments. (netsuite.com)
- [54][55] These are the top 50 countries by the total value of manufacturing output in US dollars for its noted year according to World Bank.[56] (en.wikipedia.org)
External Links
How To
How to Use lean manufacturing in the Production of Goods
Lean manufacturing refers to a method of managing that seeks to improve efficiency and decrease waste. It was first developed in Japan in the 1970s/80s by Taiichi Ahno, who was awarded the Toyota Production System (TPS), award from KanjiToyoda, the founder of TPS. Michael L. Watkins published the original book on lean manufacturing, "The Machine That Changed the World," in 1990.
Lean manufacturing refers to a set of principles that improve the quality, speed and costs of products and services. It is about eliminating defects and waste from all stages of the value stream. Lean manufacturing is called just-in-time (JIT), zero defect, total productive maintenance (TPM), or 5S. Lean manufacturing eliminates non-value-added tasks like inspection, rework, waiting.
In addition to improving product quality and reducing costs, lean manufacturing helps companies achieve their goals faster and reduces employee turnover. Lean Manufacturing is one of the most efficient ways to manage the entire value chains, including suppliers and customers as well distributors and retailers. Lean manufacturing is widely practiced in many industries around the world. Toyota's philosophy is the foundation of its success in automotives, electronics and appliances, healthcare, chemical engineers, aerospace, paper and food, among other industries.
Lean manufacturing includes five basic principles:
-
Define Value: Identify the social value of your business and what sets you apart.
-
Reduce waste - Stop any activity that isn't adding value to the supply chains.
-
Create Flow - Make sure work runs smoothly without interruptions.
-
Standardize and simplify – Make processes as repeatable and consistent as possible.
-
Develop Relationships: Establish personal relationships both with internal and external stakeholders.
Although lean manufacturing isn't a new concept in business, it has gained popularity due to renewed interest in the economy after the 2008 global financial crisis. Many businesses have adopted lean production techniques to make them more competitive. According to some economists, lean manufacturing could be a significant factor in the economic recovery.
Lean manufacturing, which has many benefits, is now a standard practice in the automotive industry. These include higher customer satisfaction levels, reduced inventory levels as well as lower operating costs.
The principles of lean manufacturing can be applied in almost any area of an organization. However, it is particularly useful when applied to the production side of an organization because it ensures that all steps in the value chain are efficient and effective.
There are three main types:
-
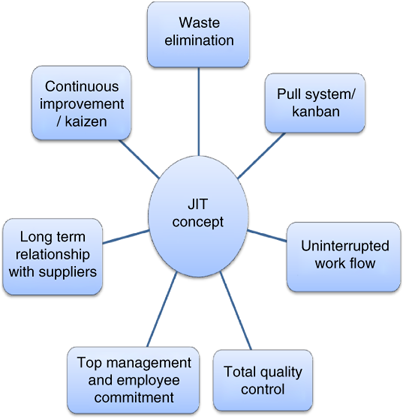
Just-in Time Manufacturing: This lean manufacturing method is commonly called "pull systems." JIT means that components are assembled at the time of use and not manufactured in advance. This approach is designed to reduce lead times and increase the availability of components. It also reduces inventory.
-
Zero Defects Manufacturing (ZDM): ZDM focuses on ensuring that no defective units leave the manufacturing facility. You should repair any part that needs to be repaired during an assembly line. This applies to finished products, which may need minor repairs before they are shipped.
-
Continuous Improvement (CI): CI aims to improve the efficiency of operations by continuously identifying problems and making changes in order to eliminate or minimize waste. Continuous Improvement (CI) involves continuous improvement in processes, people, tools, and infrastructure.