
You should evaluate the effectiveness and drawbacks of any dress code you might be considering for your workplace. Here are some things to keep in mind. Make sure you have a dress code that is both reasonable and nondiscriminatory. And listen to what your employees say. You should also consider the needs and preferences of transgender employees. You should strive to create an inclusive and transparent workplace culture.
Setting up a dress code at a business casual workplace
It's not unusual to wonder what the proper dress code is for your casual business workplace. According to OfficeTeam surveys, employees are extremely interested in business attire. Many companies have had difficulty enforcing dress codes. Here are some tips to help you design a dress code for your business.
The most important part of creating a business casual dress code is setting a tone for the office environment. Your tone will determine the culture you want to promote. For example, the Toyota Corporation uniform expresses its team-oriented culture. Casual dress codes can also communicate a fun culture.

Effectiveness of a formal dress code
It is beneficial to have a formal dress code at work. First, it sends employees a positive message. A professional dress code will make employees more likely be taken seriously and help them take their jobs more seriously. But a casual dress code can also be counterproductive. It is possible for employees to be less productive and take shortcuts in their work. Additionally, employees may lack basic respect for their employer.
Another benefit of adopting a formal dress code in the workplace is that it can improve productivity. It can make employees feel more comfortable. And it can help improve companies' image. A formal dress code is more attractive to clients and coworkers. This also helps employees avoid being noticed.
Drawbacks of a formal dress code
Establishing a dress code at work can have many benefits, but it can also have some drawbacks. It can hinder creativity, which can make it difficult for employees to express themselves and their ideas. It can reduce productivity and give job seekers a negative perception of companies with dress codes.
Secondly, it may lead to resentment. Dress codes can be helpful for businesses to present a professional image to clients. But employees might not realize the benefits of dressing like businesspeople. For small businesses, dress codes may not be necessary. However, dress codes may be necessary for larger businesses.
Incorporating formal dress codes in formal workplaces
A formal dress code is essential for managing employees' appearance. It is not a legal requirement. However, it allows the company more control over how their employees dress and conduct themselves. The dress code for the workplace may be as simple or complex as the company requires. An example of this is a company that requires employees to wear business attire on Fridays.
An employee can feel more confident and professional if they follow a formal dress code. This can encourage team members to have closer relationships. People judge credibility based on appearance. A dress code is a way to encourage consistency in the workplace.
FAQ
What are the main products of logistics?
Logistics are the activities involved in moving goods from point A to point B.
They cover all aspects of transportation, such as packing, loading, transporting and unloading.
Logisticians ensure that the product is delivered to the correct place, at the right time, and under safe conditions. Logisticians assist companies in managing their supply chains by providing information such as demand forecasts, stock levels and production schedules.
They keep track and monitor the transit of shipments, maintain quality standards, order replenishment and inventories, coordinate with suppliers, vendors, and provide support for sales and marketing.
How can manufacturing prevent production bottlenecks?
Avoiding production bottlenecks is as simple as keeping all processes running smoothly, from the time an order is received until the product ships.
This includes planning to meet capacity requirements and quality control.
This can be done by using continuous improvement techniques, such as Six Sigma.
Six Sigma management is a system that improves quality and reduces waste within your organization.
It's all about eliminating variation and creating consistency in work.
Why automate your factory?
Modern warehouses are increasingly dependent on automation. Increased demand for efficient and faster delivery has resulted in a rise in e-commerce.
Warehouses must be able to quickly adapt to changing demands. To do so, they must invest heavily in technology. Automating warehouses has many benefits. Here are some reasons why it's worth investing in automation:
-
Increases throughput/productivity
-
Reduces errors
-
Accuracy is improved
-
Safety enhancements
-
Eliminates bottlenecks
-
Companies can scale more easily
-
Makes workers more efficient
-
Provides visibility into everything that happens in the warehouse
-
Enhances customer experience
-
Improves employee satisfaction
-
Minimizes downtime and increases uptime
-
You can be sure that high-quality products will arrive on time
-
Removes human error
-
It helps ensure compliance with regulations
What is the role of a production manager?
A production planner makes sure all project elements are delivered on schedule, within budget, as well as within the agreed scope. They ensure that the product or service is of high quality and meets client requirements.
What is the responsibility of a manufacturing manager?
Manufacturing managers must ensure that manufacturing processes are efficient, effective, and cost-effective. They should be aware of any issues within the company and respond accordingly.
They should also learn how to communicate effectively with other departments, including sales and marketing.
They should be informed about industry trends and be able make use of this information to improve their productivity and efficiency.
What is the difference between Production Planning and Scheduling?
Production Planning (PP) refers to the process of determining how much production is needed at any given moment. Forecasting demand is one way to do this.
Scheduling is the process of assigning specific dates to tasks so they can be completed within the specified timeframe.
Is there anything we should know about Manufacturing Processes prior to learning about Logistics.
No. No. Understanding the manufacturing process will allow you to better understand logistics.
Statistics
- (2:04) MTO is a production technique wherein products are customized according to customer specifications, and production only starts after an order is received. (oracle.com)
- According to the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO), China is the top manufacturer worldwide by 2019 output, producing 28.7% of the total global manufacturing output, followed by the United States, Japan, Germany, and India.[52][53] (en.wikipedia.org)
- You can multiply the result by 100 to get the total percent of monthly overhead. (investopedia.com)
- Job #1 is delivering the ordered product according to specifications: color, size, brand, and quantity. (netsuite.com)
- [54][55] These are the top 50 countries by the total value of manufacturing output in US dollars for its noted year according to World Bank.[56] (en.wikipedia.org)
External Links
How To
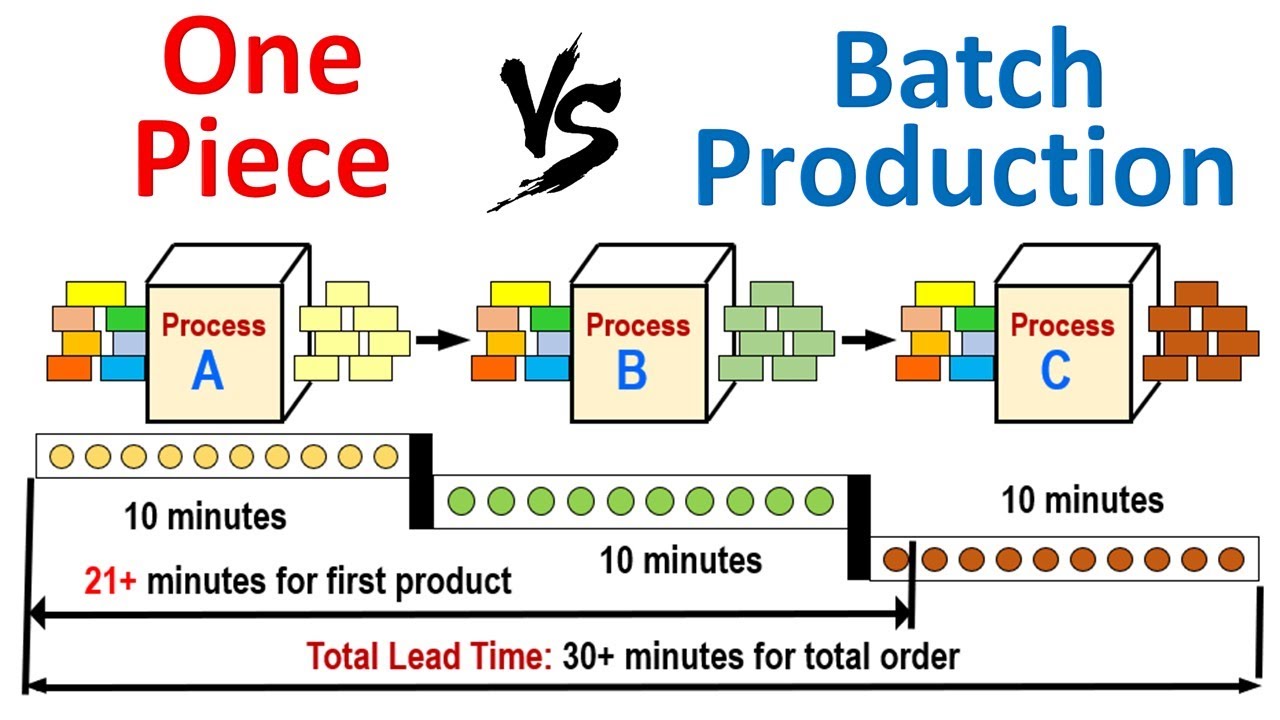
How to Use Lean Manufacturing in the Production of Goods
Lean manufacturing (or lean manufacturing) is a style of management that aims to increase efficiency, reduce waste and improve performance through continuous improvement. It was developed in Japan between 1970 and 1980 by Taiichi Ohno. TPS founder Kanji Tyoda gave him the Toyota Production System, or TPS award. The first book published on lean manufacturing was titled "The Machine That Changed the World" written by Michael L. Watkins and published in 1990.
Lean manufacturing refers to a set of principles that improve the quality, speed and costs of products and services. It emphasizes eliminating waste and defects throughout the value stream. Lean manufacturing is called just-in-time (JIT), zero defect, total productive maintenance (TPM), or 5S. Lean manufacturing eliminates non-value-added tasks like inspection, rework, waiting.
In addition to improving product quality and reducing costs, lean manufacturing helps companies achieve their goals faster and reduces employee turnover. Lean manufacturing is a great way to manage the entire value chain including customers, suppliers, distributors and retailers as well as employees. Lean manufacturing can be found in many industries. Toyota's philosophy, for example, is what has enabled it to be successful in electronics, automobiles, medical devices, healthcare and chemical engineering as well as paper and food.
Lean manufacturing is based on five principles:
-
Define value - Find out what your business contributes to society, and what makes it different from other competitors.
-
Reduce waste - Get rid of any activity that does not add value to the supply chain.
-
Create Flow. Ensure that your work is uninterrupted and flows seamlessly.
-
Standardize and simplify - Make your processes as consistent as possible.
-
Develop Relationships: Establish personal relationships both with internal and external stakeholders.
Although lean manufacturing has always been around, it is gaining popularity in recent years because of a renewed interest for the economy after 2008's global financial crisis. Many businesses have adopted lean production techniques to make them more competitive. According to some economists, lean manufacturing could be a significant factor in the economic recovery.
Lean manufacturing is now becoming a common practice in the automotive industry, with many benefits. These include better customer satisfaction and lower inventory levels. They also result in lower operating costs.
It can be applied to any aspect of an organisation. This is because it ensures efficiency and effectiveness in all stages of the value chain.
There are three main types in lean manufacturing
-
Just-in-Time Manufacturing: Also known as "pull systems", this type of lean manufacturing uses just-in-time manufacturing (JIT). JIT refers to a system in which components are assembled at the point of use instead of being produced ahead of time. This strategy aims to decrease lead times, increase availability of parts and reduce inventory.
-
Zero Defects Manufacturing - ZDM: ZDM focuses its efforts on making sure that no defective units leave a manufacturing facility. If a part is required to be repaired on the assembly line, it should not be scrapped. This applies to finished goods that may require minor repairs before shipment.
-
Continuous Improvement (CI), also known as Continuous Improvement, aims at improving the efficiency of operations through continuous identification and improvement to minimize or eliminate waste. Continuous Improvement involves continuous improvement of processes.