The manufacturing industry is constantly changing. This shift requires new skills and cutting-edge expertise. Future factories will be digitally connected, flexible, accountable, and efficient. Energy consumption and manufacturing processes must be optimised, robots and cobotics must be developed, and manufacturing processes must be traceable. Manufacturing engineers will be at the forefront. Here are three areas where you need to excel. This article will introduce these key skills and how they will influence the future of your industry.
Analyst perspectives
Analyst perspectives provide valuable insights into the future of the industry. They help to understand current trends and assess the industry's competitive dynamics. These insights give insight into the changing consumer landscape. They include attitudes and intentions as well as purchasing behavior. NPD conducts an annual survey to provide a complete picture of the industry's outlook. The country-specific forecasted categories vary for each industry. This chapter examines the role played by industry analysts in validating and generating market-based knowledge.
Consumer survey data
Prosper surveys are based on the responses of more than 71,000 adults each month. It is trended and correlated, and includes questions about consumers' emotional state, future plans, and purchasing habits. It also includes monthly data for hundreds of major retailers and brands over the past 18 years. It's the best method to discover the fundamental attitudes and spending habits in a certain market. Business owners and marketers can use consumer survey data for invaluable information.
Growth patterns in the industry
This chapter will focus on the growth patterns in industries and firms. Industry growth speed is affected by how developed countries develop financial markets. Finance-hungry sectors grow faster in countries with developed financial markets and those sectors that depend on external finance grow faster after periods of high stock market performance. These patterns match trade and developmental theories which indicate that a country’s product portfolio reflects its economic level. We will discuss here the main trends and drivers that affect industry growth.
Automation
Gartner predicts that automation is going to affect almost every occupation in the next decade. While automation can only be achieved in five percent, there are many other activities that could be automated. Most occupations are likely to be affected in some fashion, and the nature or job description of these jobs could change. The workplace will determine whether or not they adapt to change. These are five ways that automation will affect the manufacturing industry.
Hybrid workplace
To create a successful hybrid workplace, companies must listen to their employees and provide many ways to share that feedback. To gather valuable information, they can use focus groups or human resources surveys. They may also give incentives to employees such as food deliveries, financial rewards or tokens and appreciation. Companies can listen to employees and ensure that the transition to the new environment is smooth. This will create a positive experience for all.
Streaming media
The streaming media sector is a brand new industry and its future is uncertain. Many media conglomerates have begun selling short-term streaming rights in order to access three services. While streaming was initially a small market, it has become a growing industry and is set to overtake linear television in the next few decades. By 2025, almost all of the four media conglomerates' productions should be exclusive to their streaming services.
Automotive industry
How does the future look for the automotive industry? Many experts believe that it will slowly start to recover in the next decade. Automakers are currently facing many challenges. The latest technologies, like connected cars, may open up new revenue streams. The government can make emission laws more flexible, while automotive companies can increase their resilience and expand R&D. There are several reasons why the Automotive Industry could start to recover slowly over the coming decade.
FAQ
What are the 4 types of manufacturing?
Manufacturing is the process that transforms raw materials into useful products. It can involve many activities like designing, manufacturing, testing packaging, shipping, selling and servicing.
What are the 7 R's of logistics?
The acronym 7R's of Logistic is an acronym that stands for seven fundamental principles of logistics management. It was created by the International Association of Business Logisticians and published in 2004 under its "Seven Principles of Logistics Management".
The acronym is made up of the following letters:
-
Responsive - ensure all actions are legal and not harmful to others.
-
Reliable - Have confidence in your ability to fulfill all of your commitments.
-
Reasonable - use resources efficiently and don't waste them.
-
Realistic - Consider all aspects of operations, including environmental impact and cost effectiveness.
-
Respectful - Treat people fairly and equitably
-
You are resourceful and look for ways to save money while increasing productivity.
-
Recognizable - Provide value-added services to customers
What is the role and responsibility of a Production Planner?
Production planners ensure that all project aspects are completed on time, within budget and within the scope. They also ensure that the product/service meets the client’s needs.
Statistics
- Many factories witnessed a 30% increase in output due to the shift to electric motors. (en.wikipedia.org)
- It's estimated that 10.8% of the U.S. GDP in 2020 was contributed to manufacturing. (investopedia.com)
- In the United States, for example, manufacturing makes up 15% of the economic output. (twi-global.com)
- (2:04) MTO is a production technique wherein products are customized according to customer specifications, and production only starts after an order is received. (oracle.com)
- You can multiply the result by 100 to get the total percent of monthly overhead. (investopedia.com)
External Links
How To
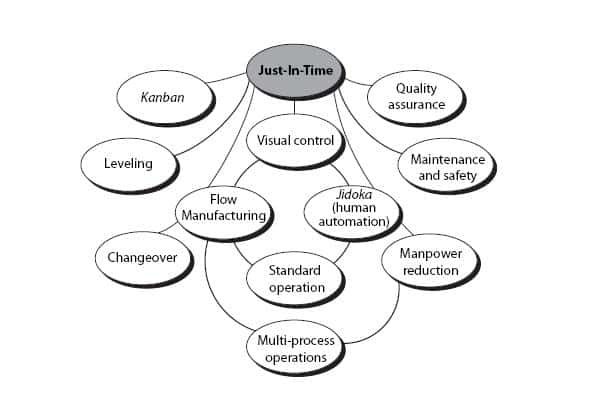
How to Use the Just-In-Time Method in Production
Just-in-time (JIT) is a method that is used to reduce costs and maximize efficiency in business processes. It allows you to get the right amount resources at the right time. This means that only what you use is charged to your account. Frederick Taylor, a 1900s foreman, first coined the term. He noticed that workers were often paid overtime when they had to work late. He concluded that if workers were given enough time before they start work, productivity would increase.
The idea behind JIT is that you should plan ahead and have everything ready so you don't waste money. The entire project should be looked at from start to finish. You need to ensure you have enough resources to tackle any issues that might arise. You will have the resources and people to solve any problems you anticipate. This will prevent you from spending extra money on unnecessary things.
There are several types of JIT techniques:
-
Demand-driven: This is a type of JIT where you order the parts/materials needed for your project regularly. This will allow for you to track the material that you have left after using it. This will let you know how long it will be to produce more.
-
Inventory-based: This is a type where you stock the materials required for your projects in advance. This allows you to forecast how much you will sell.
-
Project-driven: This is an approach where you set aside enough funds to cover the cost of your project. When you know how much you need, you'll purchase the appropriate amount of materials.
-
Resource-based JIT is the most widespread form. You assign certain resources based off demand. If you have many orders, you will assign more people to manage them. If there aren't many orders, you will assign fewer people.
-
Cost-based: This is the same as resource-based except that you don't care how many people there are but how much each one of them costs.
-
Price-based: This is similar to cost-based but instead of looking at individual workers' salaries, you look at the total company price.
-
Material-based: This is quite similar to cost-based, but instead of looking at the total cost of the company, you're concerned with how much raw materials you spend on average.
-
Time-based JIT: This is another variant of resource-based JIT. Instead of worrying about how much each worker costs, you can focus on how long the project takes.
-
Quality-based JIT - This is another form of resource-based JIT. Instead of thinking about the cost of each employee or the time it takes to produce something, you focus on how good your product quality.
-
Value-based JIT: One of the most recent forms of JIT. In this instance, you are not concerned about the product's performance or meeting customer expectations. Instead, your goal is to add value to the market.
-
Stock-based. This method is inventory-based and focuses only on the actual production at any given point. It's useful when you want maximum production and minimal inventory.
-
Just-intime planning (JIT), is a combination JIT/sales chain management. It is the process that schedules the delivery of components within a short time of their order. It is essential because it reduces lead-times and increases throughput.