
Manufacturing engineering is sometimes referred to simply as engineering production. This type is similar to other engineering fields in that it shares many of the same ideas and concepts. Engineers who specialize in this area can find their own niche within an industry and become integral to the success of a company. These engineers can ensure that a product and service meet high quality standards.
Job duties
The job of a production engineer involves coordinating and analyzing the production process, from design to implementation. This job requires a high level of attention to detail and a dedication to safety at work. Production engineers are responsible for ensuring that companies maintain high quality standards, environmental safety, as well as evaluating existing production activities in order to find ways to improve.
A production engineer helps a company produce products quickly and affordably, and they also play a key role in implementing automation. Their work may include analyzing current production processes, as well as focusing their attention on one aspect of the production process. They may also assist in the maintenance of plant software and train workers.
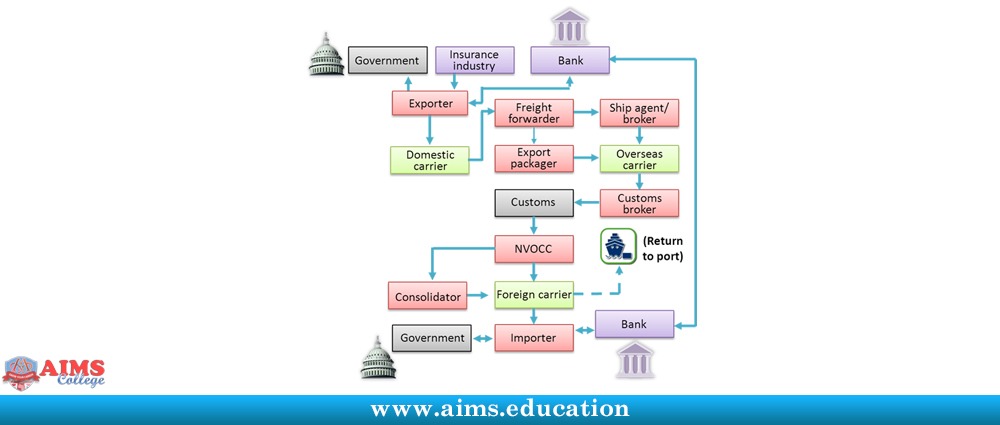
The job demands excellent communication skills. Engineers must be able explain complicated engineering concepts clearly. Engineering often involves complicated calculations and mathematics. A production engineer may use equations for determining the cost of finished products, or solving manufacturing line problems.
Education Required
The first step toward a career as a production engineer is to acquire a bachelor's degree in manufacturing or industrial engineering. A master's degree may be preferred by some employers, particularly for positions that are research-oriented in manufacturing. Additionally, it is beneficial to be proficient in a number of specialized areas.
Industrial engineers bring creativity and analysis to improve the efficiency in production processes. They seek to eliminate waste and develop new methods to use materials, equipment, and employees more efficiently. Because they must communicate complex processes to non-technical audience, they should also possess excellent communication skills. Communication skills include the ability to listen and understand others' views and opinions.
Manufacturing engineers learn hands-on skills during the degree program. Safety regulations and procedures will be covered. A Professional Engineer license issued by the National Society of Professional Engineers is required. This license is essential because it shows employers and clients that your credentials are valid. It's important to renew your licence according to state requirements.

Salary
The salary of a production engineer varies greatly, depending on location and company. Production engineers work primarily in an office environment, although they may also travel to production sites to inspect machinery and improve processes. Some production engineering employees are self-employed while others work for larger corporations. Production engineers must complete their work on time, in addition to earning a salary.
Production engineers work in collaboration with other professionals to ensure the safety and quality of the final product. They will also work closely with designers to ensure the most efficient production processes. They may also be responsible for maintaining safety standards and training factory workers in safety procedures. This job description isn't exhaustive, but it gives an idea of the duties and responsibilities of a production engineer.
The salary of a production engineer depends on his or her level of experience. For entry-level producers, the salary can be as high as Rs2.5 lakhs. For mid-level engineers, the salary can rise to Rs3.8 lakhs. An experienced production engineer can expect to earn Rs6.1 lakhs each year.
FAQ
What skills does a production planner need?
Being a production planner is not easy. You need to be organized and flexible. You must also be able to communicate effectively with clients and colleagues.
Is there anything we should know about Manufacturing Processes prior to learning about Logistics.
No. It doesn't matter if you don't know anything about manufacturing before you learn about logistics. It is important to know about the manufacturing processes in order to understand how logistics works.
Why should you automate your warehouse?
Modern warehousing has seen automation take center stage. With the rise of ecommerce, there is a greater demand for faster delivery times as well as more efficient processes.
Warehouses have to be flexible to meet changing requirements. Technology investment is necessary to enable warehouses to respond quickly to changing demands. Automation of warehouses offers many benefits. These are some of the benefits that automation can bring to warehouses:
-
Increases throughput/productivity
-
Reduces errors
-
Improves accuracy
-
Boosts safety
-
Eliminates bottlenecks
-
Allows companies scale more easily
-
Makes workers more efficient
-
Provides visibility into everything that happens in the warehouse
-
Enhances customer experience
-
Improves employee satisfaction
-
It reduces downtime, and increases uptime
-
High quality products delivered on-time
-
Human error can be eliminated
-
This helps to ensure compliance with regulations
Statistics
- In 2021, an estimated 12.1 million Americans work in the manufacturing sector.6 (investopedia.com)
- (2:04) MTO is a production technique wherein products are customized according to customer specifications, and production only starts after an order is received. (oracle.com)
- You can multiply the result by 100 to get the total percent of monthly overhead. (investopedia.com)
- In the United States, for example, manufacturing makes up 15% of the economic output. (twi-global.com)
- According to a Statista study, U.S. businesses spent $1.63 trillion on logistics in 2019, moving goods from origin to end user through various supply chain network segments. (netsuite.com)
External Links
How To
How to Use the Just In Time Method in Production
Just-in-time is a way to cut costs and increase efficiency in business processes. It allows you to get the right amount resources at the right time. This means that your only pay for the resources you actually use. Frederick Taylor developed the concept while working as foreman in early 1900s. After observing how workers were paid overtime for late work, he realized that overtime was a common practice. He decided that workers would be more productive if they had enough time to complete their work before they started to work.
JIT is an acronym that means you need to plan ahead so you don’t waste your money. It is important to look at your entire project from beginning to end and ensure that you have enough resources to handle any issues that may arise. If you expect problems to arise, you will be able to provide the necessary equipment and personnel to address them. This will ensure that you don't spend more money on things that aren't necessary.
There are many JIT methods.
-
Demand-driven: This is a type of JIT where you order the parts/materials needed for your project regularly. This will allow for you to track the material that you have left after using it. You'll also be able to estimate how long it will take to produce more.
-
Inventory-based: This type allows you to stock the materials needed for your projects ahead of time. This allows one to predict how much they will sell.
-
Project-driven: This is an approach where you set aside enough funds to cover the cost of your project. If you know the amount you require, you can buy the materials you need.
-
Resource-based JIT is the most widespread form. You assign certain resources based off demand. For instance, if you have a lot of orders coming in, you'll assign more people to handle them. If you don't have many orders, you'll assign fewer people to handle the workload.
-
Cost-based: This is similar to resource-based, except that here you're not just concerned about how many people you have but how much each person costs.
-
Price-based: This is a variant of cost-based. However, instead of focusing on the individual workers' costs, this looks at the total price of the company.
-
Material-based: This approach is similar to cost-based. However, instead of looking at the total cost for the company, you look at how much you spend on average on raw materials.
-
Time-based JIT is another form of resource-based JIT. Instead of focusing solely on the amount each employee costs, focus on how long it takes for the project to be completed.
-
Quality-based JIT: Another variation on resource-based JIT. Instead of thinking about the cost of each employee or the time it takes to produce something, you focus on how good your product quality.
-
Value-based JIT: One of the most recent forms of JIT. In this instance, you are not concerned about the product's performance or meeting customer expectations. Instead, your focus is on the value you bring to the market.
-
Stock-based: This inventory-based approach focuses on how many items are being produced at any one time. This is used to increase production and minimize inventory.
-
Just-in-time planning (JIT): This is a combination JIT and supply-chain management. This refers to the scheduling of the delivery of components as soon after they are ordered. It's important because it reduces lead times and increases throughput.