Manufacturing engineering is commonly referred to by the term production engineering. This type shares many ideas and concepts with other engineering areas. Engineers who specialize in this area can find their own niche within an industry and become integral to the success of a company. They can make sure that the product or service is of high quality.
Job duties
A production engineer is responsible for managing and analysing all aspects of the production process, including design and implementation. This job requires great attention to detail and a commitment towards safety at the workplace. Production engineers also ensure that their company maintains high quality standards and environmental safety, and they evaluate existing production activities to identify ways to improve them.
A production engineer helps a company produce products quickly and affordably, and they also play a key role in implementing automation. The job of a production engineer may involve them analysing current production processes and/or focusing on a particular area. They may also assist in the maintenance of plant software and train workers.
Communication skills are essential in this job. Engineers need to be able communicate complex engineering concepts in a simple and understandable way. This is because engineering requires complex calculations and math. Production engineers may use equations in order to predict the final product's cost or to solve problems within their manufacturing lines.
Education Required
First, earn a bachelor’s degree in industrial or manufacturing engineering to get a job as a production engineer. Some employers may prefer a master's degree, especially for research-oriented manufacturing positions. A proficiency in one or two specialized areas is also helpful.
Industrial engineers use their creativity and analytical skills to improve the efficiency of production processes. They strive to eliminate waste and create new ways to use equipment, materials, or employees more efficiently. You must have excellent communication skills to communicate complex concepts to non-technical users. Being able listen to and understand others' opinions and points of view is a key component of good communication skills.
Manufacturing engineers will receive practical training as part of the degree program. Safety regulations and procedures will be covered. A Professional Engineer license issued by the National Society of Professional Engineers is required. This license proves to employers and clients you have the right credentials. Renewing your license should be done according to the state's requirements.

Salary
The salary of a producer engineer will vary depending on the company and where you live. Production engineers are mostly employed in an office environment. However, they can also travel to manufacturing sites to inspect machinery or improve processes. Some production engineers are self-employed, while others work for larger companies. In addition to their salary, production engineers are expected to complete their work in a timely manner.
Production engineers work in collaboration with other professionals to ensure the safety and quality of the final product. To ensure the best production processes, they will work closely with designers. In some cases they will also be responsible to maintain safety standards on the factory floor as well as train workers on safe procedures. This job description isn't exhaustive, but it gives an idea of the duties and responsibilities of a production engineer.
A production engineer's salary will depend on how much experience they have. For entry-level producers, the salary can be as high as Rs2.5 lakhs. The average salary for mid-level engineering engineers is Rs3.8 lakhs. Experienced production engineers can make as much as Rs6.1 lakhs per year.
FAQ
What are the products and services of logistics?
Logistics are the activities involved in moving goods from point A to point B.
They include all aspects of transport, including packaging, loading, transporting, unloading, storing, warehousing, inventory management, customer service, distribution, returns, and recycling.
Logisticians ensure that the product is delivered to the correct place, at the right time, and under safe conditions. Logisticians assist companies in managing their supply chains by providing information such as demand forecasts, stock levels and production schedules.
They keep track and monitor the transit of shipments, maintain quality standards, order replenishment and inventories, coordinate with suppliers, vendors, and provide support for sales and marketing.
Are there any Manufacturing Processes that we should know before we can learn about Logistics?
No. It doesn't matter if you don't know anything about manufacturing before you learn about logistics. Understanding the manufacturing process will allow you to better understand logistics.
Why is logistics so important in manufacturing?
Logistics is an integral part of every business. They are essential to any business's success.
Logistics plays a significant role in reducing cost and increasing efficiency.
What can I do to learn more about manufacturing?
Practical experience is the best way of learning about manufacturing. However, if that's not possible, you can always read books or watch educational videos.
What is the difference between Production Planning and Scheduling?
Production Planning (PP), is the process of deciding what production needs to take place at any given time. Forecasting and identifying production capacity are two key elements to this process.
Scheduling refers the process by which tasks are assigned dates so that they can all be completed within the given timeframe.
Is it possible to automate certain parts of manufacturing
Yes! Yes. Automation has been around since ancient time. The Egyptians discovered the wheel thousands and years ago. Today, robots assist in the assembly of lines.
Actually, robotics can be used in manufacturing for many purposes. These include:
-
Robots for assembly line
-
Robot welding
-
Robot painting
-
Robotics inspection
-
Robots that create products
Manufacturing could also benefit from automation in other ways. 3D printing is a way to make custom products quickly and without waiting weeks or months for them to be manufactured.
Statistics
- In the United States, for example, manufacturing makes up 15% of the economic output. (twi-global.com)
- According to a Statista study, U.S. businesses spent $1.63 trillion on logistics in 2019, moving goods from origin to end user through various supply chain network segments. (netsuite.com)
- Job #1 is delivering the ordered product according to specifications: color, size, brand, and quantity. (netsuite.com)
- According to the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO), China is the top manufacturer worldwide by 2019 output, producing 28.7% of the total global manufacturing output, followed by the United States, Japan, Germany, and India.[52][53] (en.wikipedia.org)
- [54][55] These are the top 50 countries by the total value of manufacturing output in US dollars for its noted year according to World Bank.[56] (en.wikipedia.org)
External Links
How To
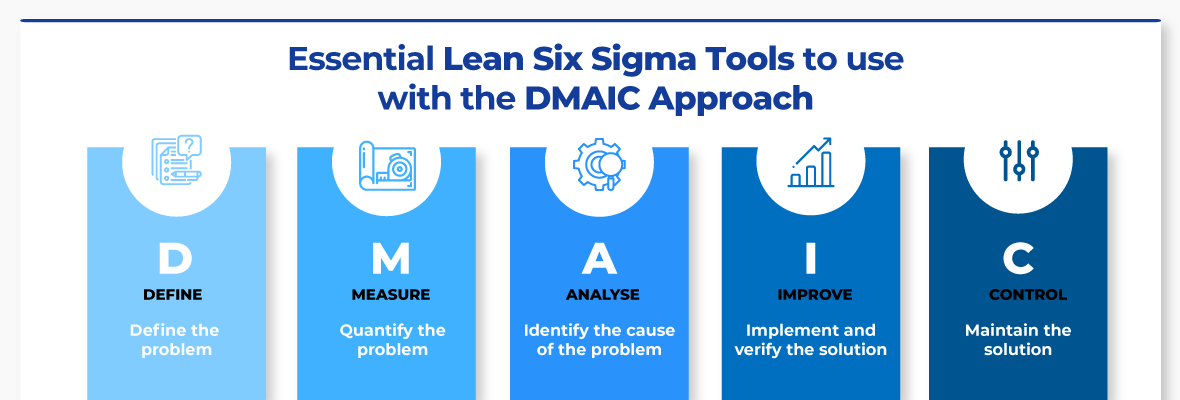
Six Sigma in Manufacturing
Six Sigma can be described as "the use of statistical process control (SPC), techniques to achieve continuous improvement." Motorola's Quality Improvement Department created Six Sigma at their Tokyo plant, Japan in 1986. Six Sigma's core idea is to improve the quality of processes by standardizing and eliminating defects. Many companies have adopted Six Sigma in recent years because they believe that there are no perfect products and services. The main goal of Six Sigma is to reduce variation from the mean value of production. This means that you can take a sample from your product and then compare its performance to the average to find out how often the process differs from the norm. If the deviation is excessive, it's likely that something needs to be fixed.
Understanding the dynamics of variability within your business is the first step in Six Sigma. Once you understand this, you can then identify the causes of variation. This will allow you to decide if these variations are random and systematic. Random variations occur when people make mistakes; systematic ones are caused by factors outside the process itself. You could consider random variations if some widgets fall off the assembly lines. You might notice that your widgets always fall apart at the same place every time you put them together.
Once you have identified the problem, you can design solutions. That solution might involve changing the way you do things or redesigning the process altogether. Once you have implemented the changes, it is important to test them again to ensure they work. If they don't work you need to rework them and come up a better plan.