
Just-in-time production is a set of principles and practices used by businesses to create goods that meet customer demand. This approach is based on effective manufacturing workflows and quality control. It allows manufacturers lower inventory levels and less warehouse space. These benefits come with lower costs.
Although JIT has been proven to reduce overall costs for many companies, implementation can be complicated. JIT is not only dependent on operations coordination, but also the efficiency of the supply chains. It is vulnerable to disruptions in the global market's economic and logistical operations. There are many tools that can help you manage the JIT challenges.
When implemented properly, JIT can significantly reduce costs. It also increases the quality of final products. This technique can also improve the efficiency of both machine and human labor. This technique also increases the speed and smoothness in the production cycle. It will reduce the time it takes to process unneeded output and also lower the environmental impact.
In Japan, just-in time production was first introduced during the rise of lean manufacturing. After World War II, Japanese organizations had to rely on scarce resources. In order to survive, they had to streamline their manufacturing processes. To maximize their output, they adopted JIT technologies.
Toyota's management team adopted the technique, and their production went from being a curiosity test to an example of success in just a few short years. This was a method that became so popular that other Japanese companies started to pay attention.
JIT has gained popularity in Japan because of its effectiveness. But before implementing this system, manufacturers should understand the risks and benefits that come along with the implementation. It is important to establish strong relationships with suppliers in order for a JIT implementation to be successful. Suppliers can minimize stock-keeping needs and increase delivery speed.
There are two basic types of JIT methods: pull and push. Push is the more conventional Make to Stock form of manufacturing. However, push puts pressure on the other areas of your business. Additionally, retooling can cost a lot. Also, the pull method relies on the actual demand.
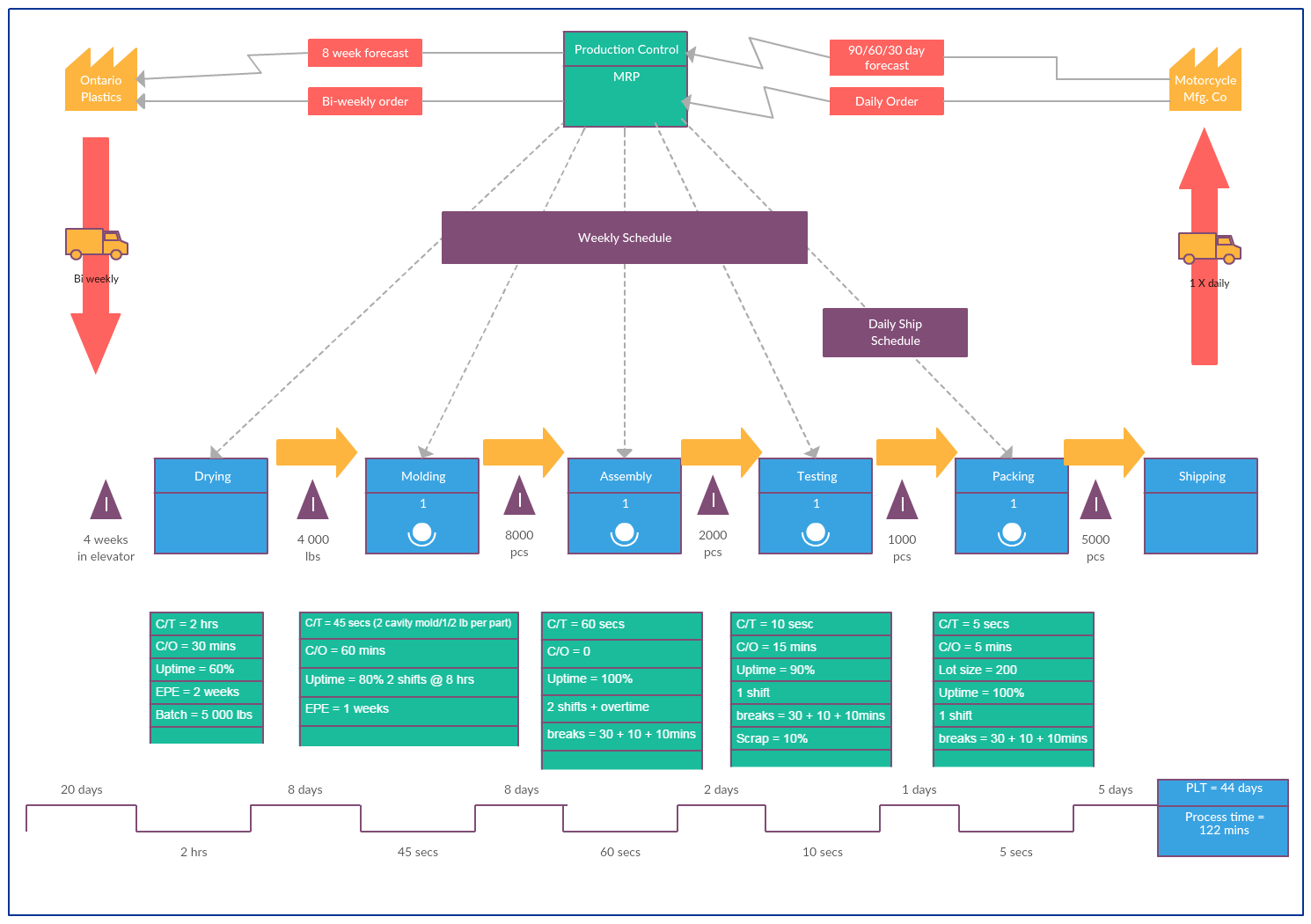
Both of these methods have been applied by many companies around the world. A successful implementation requires that all workers are empowered to resolve quality issues. JIT's success can also be affected by the complexity and time taken between manufacturer deliveries and supplier deliveries.
In order to be successful, a company should not keep any finished products or raw material stock. If it does, then it should have a small number of reusable containers called kanban.
Aside from minimizing waste, JIT also aims to maximize the efficiency of both human and machine labor. It is important that you identify and address any quality problems before they develop.
FAQ
How can manufacturing reduce production bottlenecks?
The key to avoiding bottlenecks in production is to keep all processes running smoothly throughout the entire production cycle, from the time you receive an order until the time when the product ships.
This includes planning for capacity requirements as well as quality control measures.
This can be done by using continuous improvement techniques, such as Six Sigma.
Six Sigma Management System is a method to increase quality and reduce waste throughout your organization.
It focuses on eliminating variation and creating consistency in your work.
How can manufacturing overproduction be reduced?
The key to reducing overproduction lies in developing better ways to manage inventory. This would reduce the amount of time spent on unnecessary activities such as purchasing, storing, and maintaining excess stock. By doing this, we could free up resources for other productive tasks.
Kanban systems are one way to achieve this. A Kanbanboard is a visual tool that allows you to keep track of the work being done. A Kanban system allows work items to move through several states before reaching their final destination. Each state represents a different priority level.
To illustrate, work can move from one stage or another when it is complete enough for it to be moved to a new stage. But if a task remains in the beginning stages it will stay that way until it reaches its end.
This helps to keep work moving forward while ensuring that no work is left behind. Managers can view the Kanban board to see how much work they have done. This information allows them to adjust their workflow based on real-time data.
Lean manufacturing is another way to manage inventory levels. Lean manufacturing seeks to eliminate waste from every step of the production cycle. Waste includes anything that does not add value to the product. Here are some examples of common types.
-
Overproduction
-
Inventory
-
Unnecessary packaging
-
Materials in excess
By implementing these ideas, manufacturers can improve efficiency and cut costs.
What is meant by manufacturing industries?
Manufacturing Industries is a group of businesses that produce goods for sale. Consumers are those who purchase these products. These companies employ many processes to achieve this purpose, such as production and distribution, retailing, management and so on. These companies produce goods using raw materials and other equipment. This includes all types and varieties of manufactured goods, such as food items, clothings, building supplies, furnitures, toys, electronics tools, machinery vehicles, pharmaceuticals medical devices, chemicals, among others.
What are the products of logistics?
Logistics refers to the movement of goods from one place to another.
They include all aspects associated with transport including packaging, loading transporting, unloading storage, warehousing inventory management customer service, distribution returns and recycling.
Logisticians ensure that products reach the right destination at the right moment and under safe conditions. They help companies manage their supply chain efficiency by providing information on demand forecasts, stock levels, production schedules, and availability of raw materials.
They keep track and monitor the transit of shipments, maintain quality standards, order replenishment and inventories, coordinate with suppliers, vendors, and provide support for sales and marketing.
What are the four types of manufacturing?
Manufacturing is the process by which raw materials are transformed into useful products through machines and processes. Manufacturing can include many activities such as designing and building, testing, packaging shipping, selling, servicing, and other related activities.
Statistics
- (2:04) MTO is a production technique wherein products are customized according to customer specifications, and production only starts after an order is received. (oracle.com)
- You can multiply the result by 100 to get the total percent of monthly overhead. (investopedia.com)
- According to a Statista study, U.S. businesses spent $1.63 trillion on logistics in 2019, moving goods from origin to end user through various supply chain network segments. (netsuite.com)
- In 2021, an estimated 12.1 million Americans work in the manufacturing sector.6 (investopedia.com)
- Job #1 is delivering the ordered product according to specifications: color, size, brand, and quantity. (netsuite.com)
External Links
How To
How to Use the Just In Time Method in Production
Just-in-time is a way to cut costs and increase efficiency in business processes. It is a process where you get the right amount of resources at the right moment when they are needed. This means that your only pay for the resources you actually use. Frederick Taylor developed the concept while working as foreman in early 1900s. After observing how workers were paid overtime for late work, he realized that overtime was a common practice. He concluded that if workers were given enough time before they start work, productivity would increase.
The idea behind JIT is that you should plan ahead and have everything ready so you don't waste money. Also, you should look at the whole project from start-to-finish and make sure you have the resources necessary to address any issues. You will have the resources and people to solve any problems you anticipate. This way you won't be spending more on things that aren’t really needed.
There are several types of JIT techniques:
-
Demand-driven: This type of JIT allows you to order the parts/materials required for your project on a regular basis. This will allow you to track how much material you have left over after using it. You'll also be able to estimate how long it will take to produce more.
-
Inventory-based: You stock materials in advance to make your projects easier. This allows you to forecast how much you will sell.
-
Project-driven: This approach involves setting aside sufficient funds to cover your project's costs. Once you have an idea of how much material you will need, you can purchase the necessary materials.
-
Resource-based: This is the most common form of JIT. You allocate resources based on the demand. You will, for example, assign more staff to deal with large orders. You'll have fewer orders if you have fewer.
-
Cost-based: This is the same as resource-based except that you don't care how many people there are but how much each one of them costs.
-
Price-based: This approach is very similar to the cost-based method except that you don't look at individual workers costs but the total cost of the company.
-
Material-based is an alternative to cost-based. Instead of looking at the total cost in the company, this method focuses on the average amount of raw materials that you consume.
-
Time-based JIT is another form of resource-based JIT. Instead of focusing only on how much each employee is costing, you should focus on how long it takes to complete your project.
-
Quality-based: This is yet another variation of resource-based JIT. Instead of thinking about the cost of each employee or the time it takes to produce something, you focus on how good your product quality.
-
Value-based JIT is the newest form of JIT. In this case, you're not concerned with how well the products perform or whether they meet customer expectations. Instead, you are focused on adding value to the marketplace.
-
Stock-based: This inventory-based approach focuses on how many items are being produced at any one time. This is used to increase production and minimize inventory.
-
Just-intime planning (JIT), is a combination JIT/sales chain management. It's the process of scheduling delivery of components immediately after they are ordered. It reduces lead times and improves throughput.