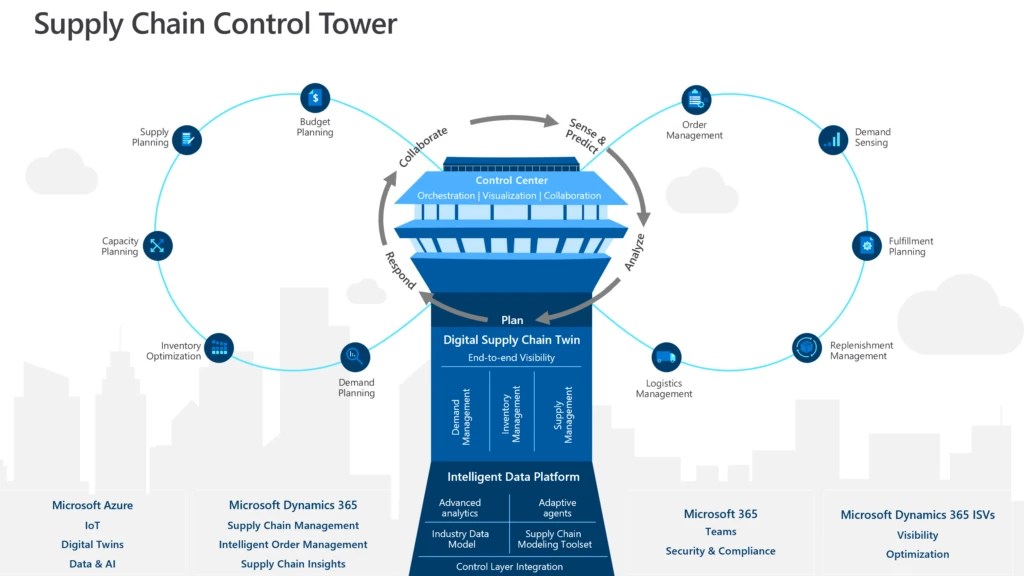
The field of manufacturing engineering often goes by the name production engineering. This type of engineering has many similarities to other engineering fields. This area of engineering is a great way to find your niche and be a part of the company's success. These engineers can ensure that a product and service meet high quality standards.
Your job duties
A production engineer is responsible for managing and analysing all aspects of the production process, including design and implementation. This job requires a high level of attention to detail and a dedication to safety at work. Production engineers are responsible for ensuring that companies maintain high quality standards, environmental safety, as well as evaluating existing production activities in order to find ways to improve.
Production engineers help companies produce products efficiently and cost-effectively. The job of a production engineer may involve them analysing current production processes and/or focusing on a particular area. They can also adjust plant software or train production workers.

Communication skills are essential in this job. Engineers must be able understand complex engineering concepts. Engineering often involves complicated calculations and mathematics. A production engineer may use equations to determine how much a finished product will cost, or to solve manufacturing line problems.
Education Required
The first step toward a career as a production engineer is to acquire a bachelor's degree in manufacturing or industrial engineering. In order to be considered for research-oriented jobs in manufacturing, employers might prefer a master's level. It's also helpful to possess proficiency in one or more specialized areas.
Industrial engineers use their creativity and analytical skills to improve the efficiency of production processes. They strive to eliminate waste and create new ways to use equipment, materials, or employees more efficiently. They must also have good communication skills, as they must be able to explain complex processes to non-technical audiences. Good communication skills also involve being able to listen carefully and fully understand the views and opinions of others.
During the degree program, manufacturing engineers receive hands-on training. They will also learn safety procedures and regulations. They will need to apply for a Professional Engineer licence issued by National Society of Professional Engineers. This license is crucial because it will show employers and clients that the credentials you have are legitimate. It is also important that you renew your license according state requirements.
Salary
The salary of production engineers varies depending on their location and company. Production engineers are mostly employed in an office environment. However, they can also travel to manufacturing sites to inspect machinery or improve processes. Some production engineers work for themselves, while others are employed by larger companies. In addition to their salary, production engineers are expected to complete their work in a timely manner.
Production engineers work closely with other professionals during the production process to ensure quality and safety. They will also work closely with designers to ensure the most efficient production processes. In some cases, they may be responsible for maintaining safety standards in the factory and training workers about proper safety procedures. Although the job description of a Production Engineer isn't comprehensive, it will give you an idea about their duties and responsibilities.
The salary of a production engineering worker depends on the amount of experience. For entry-level producers, the salary can be as high as Rs2.5 lakhs. The salary for mid-level engineers can reach Rs3.8 lakhs. For experienced production engineers, the annual salary can rise to Rs3.8 lakhs.
FAQ
What does warehouse mean?
A warehouse or storage facility is where goods are stored before they are sold. It can be an outdoor or indoor area. Sometimes, it can be both an indoor and outdoor space.
How can we improve manufacturing efficiency?
The first step is to identify the most important factors affecting production time. We must then find ways that we can improve these factors. If you don't know where to start, then think about which factor(s) have the biggest impact on production time. Once you have identified the factors, then try to find solutions.
What are the jobs in logistics?
There are different kinds of jobs available in logistics. Here are some examples:
-
Warehouse workers – They load, unload and transport pallets and trucks.
-
Transport drivers - These are people who drive trucks and trailers to transport goods or perform pick-ups.
-
Freight handlers: They sort and package freight in warehouses.
-
Inventory managers: They are responsible for the inventory and management of warehouses.
-
Sales reps are people who sell products to customers.
-
Logistics coordinators - They organize and plan logistics operations.
-
Purchasing agents - They purchase goods and services needed for company operations.
-
Customer service agents - They answer phone calls and respond to emails.
-
Shippers clerks - They process shipping order and issue bills.
-
Order fillers - They fill orders based on what is ordered and shipped.
-
Quality control inspectors – They inspect incoming and outgoing products to ensure that there are no defects.
-
Others - There is a variety of other jobs in logistics. These include transportation supervisors and cargo specialists.
Statistics
- Job #1 is delivering the ordered product according to specifications: color, size, brand, and quantity. (netsuite.com)
- According to the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO), China is the top manufacturer worldwide by 2019 output, producing 28.7% of the total global manufacturing output, followed by the United States, Japan, Germany, and India.[52][53] (en.wikipedia.org)
- (2:04) MTO is a production technique wherein products are customized according to customer specifications, and production only starts after an order is received. (oracle.com)
- [54][55] These are the top 50 countries by the total value of manufacturing output in US dollars for its noted year according to World Bank.[56] (en.wikipedia.org)
- In 2021, an estimated 12.1 million Americans work in the manufacturing sector.6 (investopedia.com)
External Links
How To
How to use Lean Manufacturing in the production of goods
Lean manufacturing is a management style that aims to increase efficiency and reduce waste through continuous improvement. It was developed in Japan between 1970 and 1980 by Taiichi Ohno. TPS founder Kanji Tyoda gave him the Toyota Production System, or TPS award. Michael L. Watkins published the book "The Machine That Changed the World", which was the first to be published about lean manufacturing.
Lean manufacturing refers to a set of principles that improve the quality, speed and costs of products and services. It emphasizes reducing defects and eliminating waste throughout the value chain. The five-steps of Lean Manufacturing are just-in time (JIT), zero defect and total productive maintenance (TPM), as well as 5S. Lean manufacturing seeks to eliminate non-value added activities, such as inspection, work, waiting, and rework.
In addition to improving product quality and reducing costs, lean manufacturing helps companies achieve their goals faster and reduces employee turnover. Lean manufacturing has been deemed one of the best ways to manage the entire value-chain, including customers, distributors as well retailers and employees. Lean manufacturing practices are widespread in many industries. Toyota's philosophy is the foundation of its success in automotives, electronics and appliances, healthcare, chemical engineers, aerospace, paper and food, among other industries.
Lean manufacturing is based on five principles:
-
Define Value - Determine the value that your business brings to society. Also, identify what sets you apart from your competitors.
-
Reduce Waste – Eliminate all activities that don't add value throughout the supply chain.
-
Create Flow. Ensure that your work is uninterrupted and flows seamlessly.
-
Standardize and simplify - Make your processes as consistent as possible.
-
Develop Relationships: Establish personal relationships both with internal and external stakeholders.
Although lean manufacturing has always been around, it is gaining popularity in recent years because of a renewed interest for the economy after 2008's global financial crisis. Many businesses have adopted lean production techniques to make them more competitive. According to some economists, lean manufacturing could be a significant factor in the economic recovery.
Lean manufacturing is now becoming a common practice in the automotive industry, with many benefits. These include improved customer satisfaction, reduced inventory levels, lower operating costs, increased productivity, and better overall safety.
The principles of lean manufacturing can be applied in almost any area of an organization. Because it makes sure that all value chains are efficient and effectively managed, Lean Manufacturing is particularly helpful for organizations.
There are three main types of lean manufacturing:
-
Just-in-Time Manufacturing: Also known as "pull systems", this type of lean manufacturing uses just-in-time manufacturing (JIT). JIT refers to a system in which components are assembled at the point of use instead of being produced ahead of time. This approach reduces lead time, increases availability and reduces inventory.
-
Zero Defects Manufacturing, (ZDM): ZDM is focused on ensuring that no defective products leave the manufacturing facility. It is better to repair a part than have it removed from the production line if it needs to be fixed. This is also true for finished products that require minor repairs before shipping.
-
Continuous Improvement (CI), also known as Continuous Improvement, aims at improving the efficiency of operations through continuous identification and improvement to minimize or eliminate waste. Continuous improvement refers to continuous improvement of processes as well people and tools.