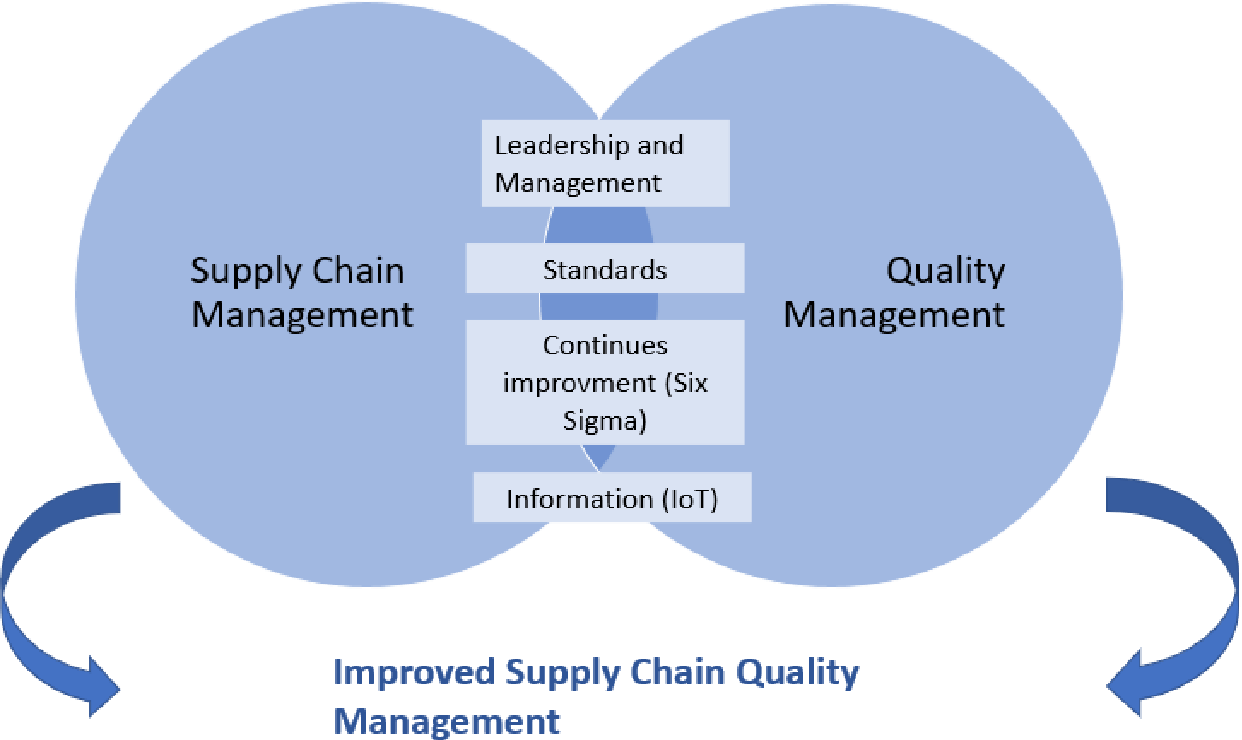
Consider lean manufacturing if you are looking to reduce costs, speed up lead times, minimize setup time, and maximize turnaround time. The benefits of using lean manufacturing are obvious: they cut costs and increase lead times while improving customer experiences. These are the key benefits of lean manufacturing, which can help you grow your business. Three reasons lean manufacturing is the best way for you to create products and cut costs if you are still skeptical.
Reduced costs
Lean manufacturing can lead to significant efficiencies. By reducing defects and rework, manufacturers can reduce their direct labor cost. As a result, labor costs become less of a motivating factor in decision-making. The elimination of hazardous waste is another benefit. The cost of direct labor in many industries is less than 15%. This makes outsourcing to low-cost areas more difficult. This can reduce overall manufacturing costs and improve customer service.
This improves lead times
Lean manufacturing has many benefits, including the ability reduce waste and increase lead times. It's a philosophy that focuses on continuous improvement (or kaizen). It aggregates the talents of employees and promotes employee accountability and collaboration. It can increase lead times up to 20% Lean manufacturing allows you to make small changes often to improve product quality and efficiency.
Shortens set-up times
The best way to shorten the time required to produce a product, is to reduce set-up periods. The time it takes for a product to be switched from its last item to the new one is called setup time. It includes the preparation, replacement, or location activities. These activities can be either internal or external. External setup activities can be done while the process is still operating.
Reduces time it takes to get to market
The concept of Lean manufacturing, or the process of continuous improvement, was developed in Japan during the rebuilding period after World War II. It was designed to increase competitiveness and decrease lead times. By shortening the time it takes for a product to reach the market, companies can meet customer demands and increase profitability. This approach to production can not only improve efficiency of the manufacturing process, but also make the entire facility more efficient.
Improves product quality
The process of reducing waste, improving product quality, and minimizing costs are all important to the success of lean manufacturing. It is used by both large manufacturers and smaller businesses alike. It decreases lead times, costs, and labor. Read on for more information on how lean manufacturing can improve your business. Here are a few of the key areas to focus on. Lean principles can help reduce lead time by 90%, improve product quality and lower your costs.
Reduces indirect labor costs
Low indirect labor costs are the low hanging fruit of lean manufacturing. True lean companies do not pay too much attention to direct labor efficiency. Instead, they look for ways of reducing indirect labor costs. This involves eliminating the need for maintenance, inspection, management and material handling. It also means that production decisions are taken on the production floor. Toyota and other lean manufacturers use this same approach. In this article, we'll examine how lean production can lower indirect labor expenses.
FAQ
Is it possible to automate certain parts of manufacturing
Yes! Since ancient times, automation has been in existence. The Egyptians invented the wheel thousands of years ago. To help us build assembly lines, we now have robots.
In fact, there are several applications of robotics in manufacturing today. These include:
-
Automated assembly line robots
-
Robot welding
-
Robot painting
-
Robotics inspection
-
Robots that produce products
There are many other examples of how manufacturing could benefit from automation. 3D printing, for example, allows us to create custom products without waiting for them to be made.
What are manufacturing & logistics?
Manufacturing refers the process of producing goods from raw materials through machines and processes. Logistics is the management of all aspects of supply chain activities, including procurement, production planning, distribution, warehousing, inventory control, transportation, and customer service. Manufacturing and logistics can often be grouped together to describe a larger term that covers both the creation of products, and the delivery of them to customers.
What kind of jobs are there in logistics?
There are many kinds of jobs available within logistics. Some of them are:
-
Warehouse workers - They load and unload trucks and pallets.
-
Transportation drivers - They drive trucks and trailers to deliver goods and carry out pick-ups.
-
Freight handlers - They sort and pack freight in warehouses.
-
Inventory managers: They are responsible for the inventory and management of warehouses.
-
Sales reps - They sell products and services to customers.
-
Logistics coordinators are responsible for organizing and planning logistics operations.
-
Purchasing agents – They buy goods or services necessary to run a company.
-
Customer service representatives – They answer emails and phone calls from customers.
-
Shipping clerks - They process shipping orders and issue bills.
-
Order fillers - These people fill orders based on what has been ordered.
-
Quality control inspectors: They inspect outgoing and incoming products for any defects.
-
Others - There are many other types of jobs available in logistics, such as transportation supervisors, cargo specialists, etc.
What are the four types of manufacturing?
Manufacturing refers to the transformation of raw materials into useful products by using machines and processes. It involves many different activities such as designing, building, testing, packaging, shipping, selling, servicing, etc.
How does a production planner differ from a project manager?
The difference between a product planner and project manager is that a planer is typically the one who organizes and plans the entire project. A production planner, however, is mostly involved in the planning stages.
What does it take for a logistics enterprise to succeed?
To run a successful logistics company, you need a lot knowledge and skills. For clients and suppliers to be successful, you need to have excellent communication skills. You will need to know how to interpret data and draw conclusions. You must be able manage stress and pressure under pressure. To increase efficiency and creativity, you need to be creative. Strong leadership qualities are essential to motivate your team and help them achieve their organizational goals.
It is important to be organized and efficient in order to meet tight deadlines.
What is the difference between Production Planning, Scheduling and Production Planning?
Production Planning (PP) is the process of determining what needs to be produced at any given point in time. This is done through forecasting demand and identifying production capacities.
Scheduling refers the process by which tasks are assigned dates so that they can all be completed within the given timeframe.
Statistics
- According to the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO), China is the top manufacturer worldwide by 2019 output, producing 28.7% of the total global manufacturing output, followed by the United States, Japan, Germany, and India.[52][53] (en.wikipedia.org)
- Many factories witnessed a 30% increase in output due to the shift to electric motors. (en.wikipedia.org)
- [54][55] These are the top 50 countries by the total value of manufacturing output in US dollars for its noted year according to World Bank.[56] (en.wikipedia.org)
- (2:04) MTO is a production technique wherein products are customized according to customer specifications, and production only starts after an order is received. (oracle.com)
- In 2021, an estimated 12.1 million Americans work in the manufacturing sector.6 (investopedia.com)
External Links
How To
How to Use lean manufacturing in the Production of Goods
Lean manufacturing (or lean manufacturing) is a style of management that aims to increase efficiency, reduce waste and improve performance through continuous improvement. It was created in Japan by Taiichi Ohno during the 1970s and 80s. He received the Toyota Production System award (TPS), from Kanji Toyoda, founder of TPS. Michael L. Watkins published the original book on lean manufacturing, "The Machine That Changed the World," in 1990.
Lean manufacturing refers to a set of principles that improve the quality, speed and costs of products and services. It emphasizes reducing defects and eliminating waste throughout the value chain. Lean manufacturing is also known as just in time (JIT), zero defect total productive maintenance(TPM), and five-star (S). Lean manufacturing is about eliminating activities that do not add value, such as inspection, rework, and waiting.
Lean manufacturing improves product quality and costs. It also helps companies reach their goals quicker and decreases employee turnover. Lean Manufacturing is one of the most efficient ways to manage the entire value chains, including suppliers and customers as well distributors and retailers. Many industries worldwide use lean manufacturing. Toyota's philosophy, for example, is what has enabled it to be successful in electronics, automobiles, medical devices, healthcare and chemical engineering as well as paper and food.
Lean manufacturing is based on five principles:
-
Define Value- Identify the added value your company brings to society. What makes you stand out from your competitors?
-
Reduce Waste - Remove any activity which doesn't add value to your supply chain.
-
Create Flow. Ensure that your work is uninterrupted and flows seamlessly.
-
Standardize & simplify - Make processes consistent and repeatable.
-
Build Relationships- Develop personal relationships with both internal as well as external stakeholders.
Although lean manufacturing isn't a new concept in business, it has gained popularity due to renewed interest in the economy after the 2008 global financial crisis. Many businesses have adopted lean manufacturing techniques to help them become more competitive. Economists think that lean manufacturing is a crucial factor in economic recovery.
Lean manufacturing has many benefits in the automotive sector. These include better customer satisfaction and lower inventory levels. They also result in lower operating costs.
It can be applied to any aspect of an organisation. However, it is particularly useful when applied to the production side of an organization because it ensures that all steps in the value chain are efficient and effective.
There are three main types:
-
Just-in Time Manufacturing (JIT), also known as "pull system": This form of lean manufacturing is often referred to simply as "pull". JIT is a process in which components can be assembled at the point they are needed, instead of being made ahead of time. This approach reduces lead time, increases availability and reduces inventory.
-
Zero Defects Manufacturing - ZDM: ZDM focuses its efforts on making sure that no defective units leave a manufacturing facility. It is better to repair a part than have it removed from the production line if it needs to be fixed. This applies to finished goods that may require minor repairs before shipment.
-
Continuous Improvement: Continuous Improvement aims to improve efficiency by continually identifying problems and making adjustments to eliminate or minimize waste. Continuous Improvement (CI) involves continuous improvement in processes, people, tools, and infrastructure.