The director of manufacturing oversees the company's production process. This is a crucial role as they oversee the entire manufacturing process, from design to production. The ideal candidate should have extensive manufacturing experience and be proficient in new technologies in order to succeed in this position. Examples of such technologies are robotics and 3-D printing. An asset to any company is a director who can keep up with new technologies. As the manufacturing industry continues to evolve, the director's role will become increasingly complex, as he or she must work with the engineering and operations departments, as well as putting a greater emphasis on quality control within the manufacturing plant.
Salary for a director in manufacturing
The region in which a Director or Manufacturing is located can have a significant impact on their salary. Many directors receive compensation in the low six-figures, with some earning significantly more than others. Based on years of education and experience, the salary of a Director in Manufacturing can also vary. Here are some factors that could impact your salary.
Although the salary of a Director of Manufacturing is variable, it is generally higher for those with more experience. The cost of living and the location can also impact salary. A large city may offer higher salaries. However, you should be aware of the fact that your salary may not cover living costs. Always be willing to negotiate for a higher salary, if offered.
A Director of Manufacturing Operations can earn between $181 500 and $66,000 annually. The salary of a Director Manufacturing Operations is highly variable. It can vary by up 8% among different cities. A director of manufacturing operations in Fremont, CA can earn between $128,493 and $164,500, which is considerably more than the national average. However, the salary for a Director of Manufacturing Operations varies greatly depending on the location, experience level, and company.
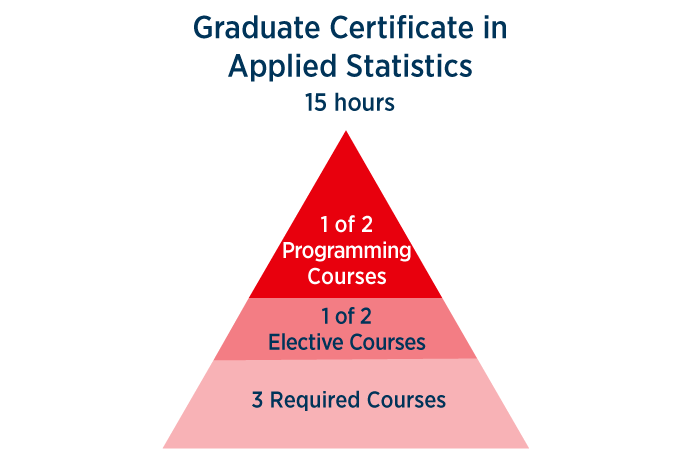
Education necessary
The director for manufacturing is responsible in managing a manufacturing plant and supervising the production process. Some of the duties of this position include hiring new employees, overseeing quality assurance, collaborating with designers, and meeting operations standards. A director in manufacturing typically reports directly to the senior management team. This person executes policies and sales initiatives. Candidates should have previous experience in manufacturing, and be able to communicate effectively. There are different educational requirements to become a director in manufacturing.

Although a graduate degree in engineering is not always required for director of manufacturing jobs, a post-secondary education in a related field will greatly enhance your skill set and knowledge base. An MBA program is an excellent choice for this role, since it allows candidates to learn more about management, business administration, and economics. In the end, you will manage a diverse team of people.
You will collaborate closely with engineers and designers as a director for manufacturing during the product development phase. This stage is where you will evaluate new manufacturing processes and ensure high quality standards. In addition to overseeing the production process, successful directors serve as coaches for employees. They will mentor them on best practices and risk mitigation. In addition to overseeing the entire production process, a manufacturing director must be able to develop strong problem-solving skills.
Experience required
A bachelor's degree in a relevant field and five to 10 years of progressive work experience are often necessary for this position. In general, manufacturing companies prefer to hire employees for this job. A strong understanding of the manufacturing process is essential. Some employers may prefer a graduate certificate. Additional training may be required for candidates in their chosen field.

The director of manufacturing supervises the production process. This includes supervisors, engineers, workers, and supervisors. They may be responsible in solving problems and creating solutions. They could also be responsible, in addition to supervising production, for creating and implementing quality-control programmes. The director of manufacturing reports directly the top executive of the manufacturing company. Experience in manufacturing is an absolute must. This position can be made more successful if you have experience in manufacturing management.
Experience as a manufacturing director essential. Directors must have a minimum of 10 years of experience in a manufacturing context. Some of these people may have started as manufacturing supervisors or technicians. They must also be able to communicate well. The director of production should also have an in-depth understanding of the business strategy. A director of Manufacturing must also be able to communicate effectively with other departments. This director supervises the production process to ensure it meets the highest quality standards.
FAQ
Why is logistics important for manufacturing?
Logistics are essential to any business. Logistics can help you achieve amazing results by helping to manage product flow from raw materials to finished products.
Logistics plays a significant role in reducing cost and increasing efficiency.
What is production planning?
Production Planning includes planning for all aspects related to production. This document ensures that everything is prepared and available when you are ready for shooting. It should also contain information on achieving the best results on set. It should include information about shooting locations, casting lists, crew details, equipment requirements, and shooting schedules.
The first step in filming is to define what you want. You may have already chosen the location you want, or there are locations or sets you prefer. Once you have identified your locations and scenes it's time to begin figuring out what elements you will need for each one. Perhaps you have decided that you need to buy a car but aren't sure which model. To narrow your options, you can search online for available models.
After you have selected the car you want, you can begin to think about additional features. You might need to have people in the front seats. You might also need someone to help you get around the back. Maybe you'd like to change the interior from black to a white color. These questions will help guide you in determining the ideal look and feel for your car. You can also think about the type of shots you want to get. Do you want to film close-ups, or wider angles? Maybe you want to show your engine or the steering wheel. These details will help identify the exact car you wish to film.
Once you have determined all of the above, you can move on to creating a schedule. You can create a schedule that will outline when you must start and finish your shoots. Each day will include the time when you need to arrive at the location, when you need to leave and when you need to return home. So everyone is clear about what they need to do. Hire extra staff by booking them ahead of time. It is not worth hiring someone who won’t show up because you didn’t tell him.
Also, consider how many days you will be filming your schedule. Some projects are quick and easy, while others take weeks. While creating your schedule, it is important to remember whether you will require more than one shot per day. Multiple takes at the same place will result in higher costs and longer completion times. If you aren't sure whether you need multiple shots, it is best to take fewer photos than you would like.
Budget setting is another important aspect in production planning. You will be able to manage your resources if you have a realistic budget. It is possible to reduce the budget at any time if you experience unexpected problems. It is important to not overestimate how much you will spend. Underestimating the cost will result in less money after you have paid for other items.
Production planning is a very detailed process, but once you understand how everything works together, it becomes easier to plan future projects.
What are manufacturing & logistics?
Manufacturing is the act of producing goods from raw materials using machines and processes. Logistics encompasses the management of all aspects associated with supply chain activities such as procurement, production planning, distribution and inventory control. It also includes customer service. Logistics and manufacturing are often referred to as one thing. It encompasses both the creation of products and their delivery to customers.
What does warehouse refer to?
A warehouse or storage facility is where goods are stored before they are sold. It can be indoors or out. It may also be an indoor space or an outdoor area.
Statistics
- According to the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO), China is the top manufacturer worldwide by 2019 output, producing 28.7% of the total global manufacturing output, followed by the United States, Japan, Germany, and India.[52][53] (en.wikipedia.org)
- According to a Statista study, U.S. businesses spent $1.63 trillion on logistics in 2019, moving goods from origin to end user through various supply chain network segments. (netsuite.com)
- In the United States, for example, manufacturing makes up 15% of the economic output. (twi-global.com)
- Job #1 is delivering the ordered product according to specifications: color, size, brand, and quantity. (netsuite.com)
- It's estimated that 10.8% of the U.S. GDP in 2020 was contributed to manufacturing. (investopedia.com)
External Links
How To
How to Use the Just-In-Time Method in Production
Just-in-time is a way to cut costs and increase efficiency in business processes. It's the process of obtaining the right amount and timing of resources when you need them. This means that your only pay for the resources you actually use. Frederick Taylor was the first to coin this term. He developed it while working as a foreman during the early 1900s. He noticed that workers were often paid overtime when they had to work late. He realized that workers should have enough time to complete their jobs before they begin work. This would help increase productivity.
JIT is a way to plan ahead and make sure you don't waste any money. Look at your entire project, from start to end. Make sure you have enough resources in place to deal with any unexpected problems. If you expect problems to arise, you will be able to provide the necessary equipment and personnel to address them. You won't have to pay more for unnecessary items.
There are many JIT methods.
-
Demand-driven: This is a type of JIT where you order the parts/materials needed for your project regularly. This will let you track the amount of material left over after you've used it. This will allow you to calculate how long it will take to make more.
-
Inventory-based : You can stock the materials you need in advance. This allows for you to anticipate how much you can sell.
-
Project-driven: This method allows you to set aside enough funds for your project. Knowing how much money you have available will help you purchase the correct amount of materials.
-
Resource-based JIT is the most widespread form. You assign certain resources based off demand. If you have many orders, you will assign more people to manage them. If you don’t have many orders you will assign less people to the work.
-
Cost-based: This is similar to resource-based, except that here you're not just concerned about how many people you have but how much each person costs.
-
Price-based: This is similar to cost-based but instead of looking at individual workers' salaries, you look at the total company price.
-
Material-based: This is quite similar to cost-based, but instead of looking at the total cost of the company, you're concerned with how much raw materials you spend on average.
-
Time-based JIT is another form of resource-based JIT. Instead of focusing on the cost of each employee, you will focus on the time it takes to complete a project.
-
Quality-based JIT: Another variation on resource-based JIT. Instead of thinking about how much each employee costs or how long it takes to manufacture something, you think about how good the quality of your product is.
-
Value-based: This is one of the newest forms of JIT. This is where you don't care about how the products perform or whether they meet customers' expectations. Instead, your focus is on the value you bring to the market.
-
Stock-based: This is an inventory-based method that focuses on the actual number of items being produced at any given time. It's used when you want to maximize production while minimizing inventory.
-
Just-in-time planning (JIT): This is a combination JIT and supply-chain management. It refers to the process of scheduling the delivery of components as soon as they are ordered. It's important as it reduces leadtimes and increases throughput.